Welcome to our article on candidiasis, a fungal skin infection that can cause discomfort and irritation. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for candidiasis. Whether you’re dealing with candidiasis yourself or want to learn more about it, we’ve got you covered.
Key Takeaways:
- Candidiasis is a fungal skin infection caused by an overgrowth of Candida on the skin.
- Common causes of candidiasis include warm weather, tight clothing, poor hygiene, obesity, antibiotic use, and a weakened immune system.
- Symptoms of candidiasis include red, itchy rash, cracked and sore skin, blisters and pustules.
- Diagnosis of candidiasis is usually made through a physical examination or skin culture.
- Treatment options for candidiasis include home remedies, improved hygiene, antifungal creams or powders, and lifestyle changes.
Different Types of Candidiasis
Candidiasis can manifest in different forms depending on the location of the infection. Understanding these different types can help in identifying and treating the specific condition effectively. The three common types of candidiasis are oral thrush, vaginal yeast infection, and cutaneous candidiasis.
Oral Thrush
Oral thrush is a type of candidiasis that affects the mouth. It is characterized by the presence of white patches inside the mouth, cracks in the corners of the mouth, and discomfort during eating or swallowing. This condition can affect people of all ages, including infants, older adults, and individuals with weakened immune systems.
Vaginal Yeast Infection
Vaginal yeast infection is another common type of candidiasis. It occurs when there is an overgrowth of Candida in the vagina, leading to symptoms such as itching, burning, and abnormal discharge. Vaginal yeast infections can cause significant discomfort and may require prompt treatment.
Cutaneous Candidiasis
Cutaneous candidiasis refers to candidiasis of the skin. It commonly affects areas of the skin that have folds, such as the groin, armpits, and under the breasts. Cutaneous candidiasis presents as red, itchy rashes, often accompanied by discomfort and irritation. It is important to note that this type of candidiasis can also affect the nails, causing nail infections.
Treating these different types of candidiasis typically involves the use of antifungal medications, such as creams or oral medications, along with proper hygiene practices. Consultation with a healthcare professional is recommended for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Causes of Candidiasis
Candidiasis, a fungal skin infection, is primarily caused by an overgrowth of the Candida fungus on the skin. This overgrowth can be triggered by various factors, including:
- Poor Hygiene: Infrequent undergarment changes and inadequate skin cleaning can create an environment conducive to Candida overgrowth.
- Candida Overgrowth: An imbalance of bacteria on the skin, caused by factors such as warm weather, tight clothing, or obesity, can contribute to Candida overgrowth.
- Antibiotic Use: The use of antibiotics, while essential for treating bacterial infections, can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria on the skin, allowing Candida to proliferate.
- Weakened Immune System: A weakened immune system, which can occur due to conditions like diabetes or pregnancy, makes individuals more susceptible to Candida overgrowth.
Candida fungi thrive in warm, moist areas of the body, which is why candidiasis often affects regions with folds of skin such as the armpits, groin, fingers, and under the breasts.
“Poor hygiene, antibiotic use, and a weakened immune system are some of the key factors that contribute to Candida overgrowth and the development of candidiasis.” – Dr. Emily Rodriguez, Dermatology Specialist
Symptoms of Candidiasis
Candidiasis, also known as a fungal skin infection, manifests with various symptoms, primarily characterized by a red and itchy rash. This discomfort can escalate, resulting in cracked, sore skin, accompanied by the formation of blisters and pustules. The prevalence of candidiasis is often observed in areas of the body with folds of skin, such as the armpits, groin, fingers, and under the breasts. Additionally, infections in the nails and corners of the mouth may also occur as a result of candidiasis.
“The main symptom of candidiasis is a rash, which is often red and itchy.”
It is important to note that while these symptoms are indicative of candidiasis, they can also resemble other conditions. Therefore, seeking professional medical advice is essential to obtain an accurate diagnosis.
Common Symptoms:
- Red rash
- Intense itching
- Cracked and sore skin
- Blisters and pustules
By recognizing these symptoms and promptly seeking medical attention, individuals can effectively manage and alleviate the discomfort caused by candidiasis.
Diagnosis of Candidiasis
To accurately diagnose candidiasis, a healthcare professional will typically conduct a physical examination of the affected area and carefully assess the appearance of the skin. This examination helps identify common symptoms, such as redness, itching, and rashes, that are indicative of candidiasis. However, since other conditions may resemble candidiasis, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
In some cases, a skin culture may be performed to confirm the presence of Candida fungi. During a skin culture, a small sample of the affected skin is collected and sent to a laboratory for testing. The sample is analyzed to determine the specific strain of Candida and to rule out any other potential skin infections. This test is particularly helpful in cases where the diagnosis is uncertain or when the symptoms persist despite initial treatments.
It is crucial to undergo a proper diagnosis as it helps healthcare professionals tailor the treatment plan to address the specific needs of the individual. By accurately identifying candidiasis, healthcare providers can ensure that appropriate antifungal medications and other treatment options are prescribed to effectively manage the infection.
Treatment of Candidiasis
Candidiasis, a fungal skin infection, can usually be effectively treated with a combination of home remedies, lifestyle changes, and over-the-counter or prescription medications. Let’s explore some of the treatment options available for managing candidiasis.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
If you have candidiasis, incorporating certain home remedies and making lifestyle adjustments can help alleviate symptoms and prevent future outbreaks. Here are some beneficial practices:
- Practice proper hygiene by regularly washing the affected skin area and ensuring it is thoroughly dried. This helps prevent excessive moisture buildup, which can contribute to Candida overgrowth.
- Change out of damp clothing, especially after exercising or sweating, to avoid creating an environment conducive to fungal growth.
- Opt for loose-fitting clothes made from breathable fabrics, as they allow better air circulation and discourage the accumulation of moisture.
- Reduce your sugar intake, as high sugar levels can contribute to yeast overgrowth. Focus on a balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Antifungal Creams and Powders
Over-the-counter antifungal creams and powders can be effective in treating mild to moderate cases of candidiasis. They contain active ingredients that specifically target the Candida fungus, helping to eliminate the infection. Common antifungal creams and powders that are often recommended for treating candidiasis include clotrimazole, miconazole, and tioconazole.
Prescription Antifungal Medications
In more severe or persistent cases of candidiasis, your healthcare provider may prescribe stronger antifungal creams or oral medications. These prescription medications are generally reserved for situations where over-the-counter treatments have not provided sufficient relief. It is important to follow the recommended treatment plan and continue any prescribed medications as directed to ensure complete recovery.
Candidiasis in Babies and Children
Candidiasis is a common fungal infection that can also affect babies and children. It presents in different forms, such as diaper rash and oral thrush, and can cause discomfort and irritation. Understanding how to identify and treat candidiasis in infants and young children is essential for their well-being.
Diaper Rash
One of the most common forms of candidiasis in babies is diaper rash. This occurs when the fungus Candida overgrows in the warm, moist environment of the diaper area. Diaper rash is characterized by red, inflamed skin, and may be accompanied by small red bumps or pustules.
- Frequently changing diapers is crucial in managing and preventing diaper rash.
- Keeping the diaper area clean and dry helps to create an unfavorable environment for Candida growth.
- Using diaper creams or ointments containing antifungal properties can help to soothe the affected area and reduce inflammation.
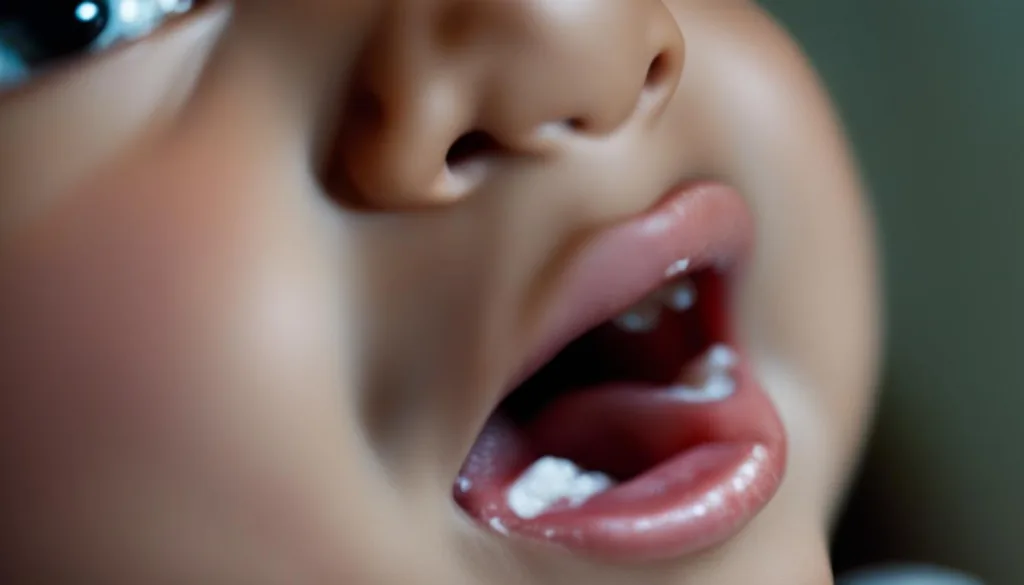
Oral Thrush
Oral thrush is another common type of candidiasis that affects babies, especially those under 6 months old. It appears as white or yellowish patches on the tongue, inner cheeks, or lips.
Oral thrush can make it difficult for babies to feed, causing discomfort and potential weight loss. It is important to treat oral thrush promptly to prevent further complications.
Antifungal medications in the form of drops or gels are commonly used to treat oral thrush in babies. These medications are usually applied directly to the affected areas in the mouth and help to eliminate the Candida fungus.
Recurrent Infections and Underlying Health Concerns
While most cases of candidiasis in babies and children are easily treated, recurrent infections may signal underlying health concerns. Children who experience frequent or persistent thrush or skin infections should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out any underlying conditions that may weaken their immune system.
| Common Candidiasis Infections in Babies and Children | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Diaper rash | Red, inflamed skin in the diaper area, small red bumps or pustules | Frequently change diapers, keep the area clean and dry, use antifungal creams or ointments |
| Oral thrush | White or yellowish patches on the tongue, inner cheeks, or lips | Antifungal medications in the form of drops or gels |
It is important for parents and caregivers to pay attention to any signs of candidiasis in babies and children and seek medical advice if symptoms persist, worsen, or recur. Early detection and appropriate treatment can help ensure the well-being and comfort of the child.
Outlook and Complications of Candidiasis
Proper treatment is key to resolving candidiasis, with most cases clearing up within one to two weeks. However, if left untreated, recovery can take longer and may lead to complications.
Even with treatment, there is a chance of recurrent infections in the future. This can occur due to factors such as underlying health conditions, weakened immune system, or the persistence of risk factors like poor hygiene or antibiotic use.
Candidiasis can be particularly concerning for individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those undergoing chemotherapy or with HIV/AIDS. In these cases, the risk of severe or life-threatening Candida infections is higher.
If you experience severe throat pain, persistent headache, or a high fever alongside candidiasis symptoms, it is vital to seek medical attention immediately. These could be indicators of a severe infection that requires prompt intervention.
Timely and appropriate treatment, along with careful management of risk factors, can help prevent complications and promote full recovery from candidiasis.
| Complications of Candidiasis | Signs and Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Recurrent infections | Repeated episodes of candidiasis despite treatment |
| Disseminated candidiasis | Spreading of candidiasis beyond the primary site of infection, usually in individuals with compromised immune systems |
| Chronic candidiasis | Persistent or long-term candidiasis that is difficult to treat and may require specialized medical care |
| Invasive candidiasis | Candida infection entering the bloodstream or affecting internal organs, posing a serious risk to overall health |
| Allergic reactions | Hypersensitivity reactions to antifungal medications or other treatments, leading to skin rashes, swelling, or difficulty breathing |
Conclusion
Candidiasis, a common fungal skin infection, can be a source of discomfort and irritation. However, with the right approach to treatment and lifestyle adjustments, it can be effectively managed.
To prevent and treat candidiasis, there are several strategies you can employ. First, incorporating home remedies such as improved hygiene practices can make a substantial difference. This includes regular washing and thorough drying of the skin, particularly in areas prone to moisture buildup. Additionally, antifungal creams or powders can be helpful in reducing the overgrowth of Candida fungi.
It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and guidance on the most suitable treatment plan for your specific case. Their expertise can determine the optimal course of action, which may involve lifestyle adjustments such as reducing sugar intake or wearing loose-fitting clothing to create an environment less conducive to fungal growth.
By taking these necessary steps to address candidiasis, individuals can experience relief from symptoms and promote overall skin health. Remember, the journey to managing and treating candidiasis effectively begins with a proactive approach and professional guidance when needed.
FAQ
What is candidiasis?
Candidiasis is a fungal skin infection that occurs when there is an overgrowth of Candida on the skin. It can manifest in different forms, such as oral thrush, vaginal yeast infection, and cutaneous candidiasis.
What causes candidiasis?
Candidiasis can be caused by factors such as warm weather, tight clothing, poor hygiene, obesity, the use of antibiotics, and a weakened immune system.
What are the symptoms of candidiasis?
The symptoms of candidiasis include red, itchy rash, cracked and sore skin, blisters and pustules. The specific symptoms can vary depending on the location of the infection.
How is candidiasis diagnosed?
Candidiasis can be diagnosed through a physical examination or a skin culture test to confirm the presence of Candida fungi.
How is candidiasis treated?
Candidiasis can usually be treated with home remedies, improved hygiene, antifungal creams or powders, and lifestyle changes. In severe cases, prescription antifungal medications may be necessary.
Can candidiasis affect babies and children?
Yes, candidiasis is common in babies and children. It can manifest as diaper rash or oral thrush and can be treated with proper hygiene and antifungal medications.
What is the outlook for candidiasis?
With proper treatment, candidiasis usually goes away within one to two weeks. However, without treatment, recovery can take longer and complications may arise.
Are there any complications associated with candidiasis?
Recurrent infections and severe infections are possible complications of candidiasis. People with compromised immune systems are at a higher risk of severe or life-threatening Candida infections.
Is there any prevention for candidiasis?
Maintaining good hygiene, avoiding tight clothing, and practicing proper skin care can help prevent candidiasis. Lifestyle adjustments, such as reducing sugar intake, can also be beneficial.

